Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a persistent inability to achieve or
maintain an erection that is firm enough to have sexual intercourse.
How common?
In a study from John Hopkins Institute in 2007, the overall
prevalence of ED in men aged above 20 years was 18.4%
suggesting that ED affects 18 million men in the USA. Among
men with diabetes, the prevalence of ED was 51.3%, so it’s a
fairly common problem.
What causes ED?
- Lifestyle choices (smoking, excessive alcohol, obesity, lack of
exercise)
- Diabetes
- Medications (blood pressure, antidepressants)
- Cardiovascular disease (high blood pressure heart disease)
- Hormone problems
- Prostate cancer treatment
- Surgery (prostate, bladder, colon)
- Spinal cord injuries

Treatment options?
Penile Doppler scan with an injection may be required occasionally
in special situations.
Whatever is causing ED, there is a treatment option that can provide
a satisfying solution.
If you try one of the treatment options listed and it doesn’t work
for you or you aren’t completely satisfied, don’t be discouraged and
give up hope.
These treatment options have varying degrees of success for each man
depending on the cause of the ED. Irreversible blood vessel or nerve
damage may impact the success of some of these treatments.
It is important to know all of your available options and discuss
them with your doctor to determine which will be appropriate for you
and your lifestyle.
Lifestyle modifications: Exercise regularly (5 times a week),
healthy weight, avoid smoking, restrict alcohol intake to 2 drinks
or less per day, adopt better sleep habits, take care of your other
health issues such as high blood sugar and heart, artery or kidney
disease.
Non-Surgical Options: Oral medications, penile injections, vacuum
erection device
Surgical option: Penile implants
Non-Surgical options
Oral medications:
These drugs are known as phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5)
inhibitors. They work to relax muscle cells in the penis for better
blood flow and to produce a rigid erection. These medicines work in
about 7 out of every 10 men with ED. They can be effective
regardless of age or race. However, they only work if a man is
sexually stimulated. Their effects last for only a set amount of
time. Men should take these medications 30-60 minutes before sexual
activity. These drugs do not treat a lack of sexual desire. As with
any drug, some men may experience side effects when taking PDE-5
inhibitors. The most common are headaches, flushing (redness) of the
face, runny or stuffy nose, upset stomach, dizziness and muscle
aches. Those side effects are usually mild-moderate, but taking
these drugs with alcohol may make them worse. Be sure you tell your
doctor about all drugs you are taking, including prescriptions,
over-the-counter medications or supplements or recreational drugs
before you take any PDE-5 inhibitors.

Penile self-injection:
Alprostadil (Prostaglandin)
Injection therapy uses a needle to inject medication directly into
the base or side of the penis. These medications improve blood flow
into the penis to cause an erection. The recommended frequency of
injection is no more than three times weekly and should produce an
erection in 5-20 minutes. Beyond a possible fear of needles, men may
experience pain, fibrosis and risk of a persistent erection with
these injections. 60-65% of men discontinue this mode of treatment
after 1 year.
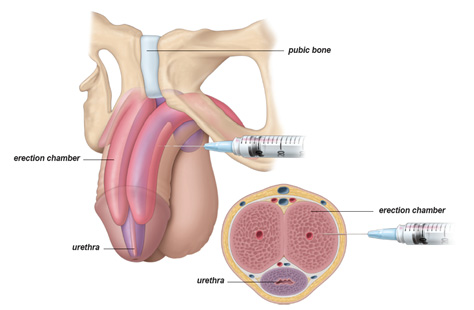
Fig: Penile Alprostadil Injection
Vacuum Erection Devices (VED):
A mechanical ED pump used to
pull blood into the penis can cause an erection. The system includes
a plastic cylinder, an external penile pump and a tension band to
place at the base of the penis. When the penis is erect, the ring is
placed at the base to maintain an erection long enough to have sex
(up to 30 minutes). This is a drug-free non-invasive method of
treatment, but the person will not be able to ejaculate soon after
the orgasm due to a constrictive ring at the penile base.
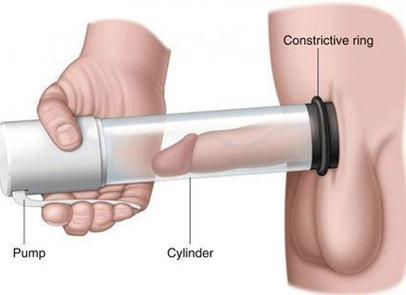
Fig: Vacuum Erection Device (VED)
Surgical option
Penile Implants:
In use since 1971, penile implants have
helped many men return to active sex life. A penile implant is a
medical implant that is implanted into the penis in the operation
theatre. The implant is entirely concealed within the body. Two
basic types of implants are available. With malleable or bendable
implants, two silicon-type cylinders are inserted into the penis. To
have an erection, a man bends his penis upward into an erect
position. The second type, an inflatable implant has a pair of
inflatable cylinders which is attached to a fluid reservoir and a
pump hidden inside the body. To have an erection, a man presses on
the pump. This transfers fluid into the cylinders, making the penis
rigid. To return the penis to a natural flaccid state, the pump is
deflated.
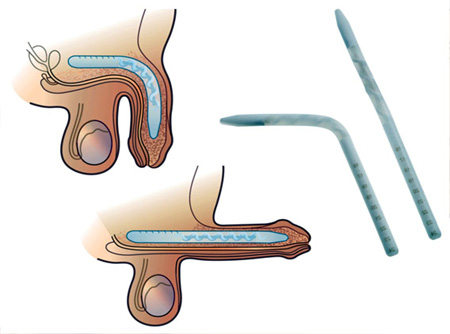
Fig: Malleable Implant

Fig: Malleable Implant- Shah
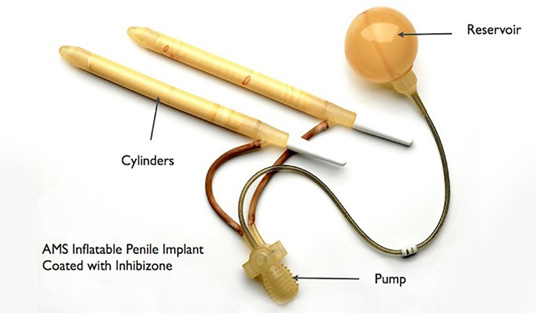
Fig: Inflatable penile implant
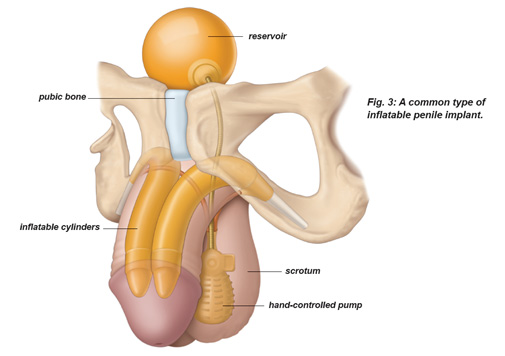
Fig: Inflatable penile Implant in anatomical
position
Features of Penile Implant Surgery:
- Permanent ED Treatment
- Small external scar
- Concealed within the body
- Maintain erection as long as desired
- Spontaneous-sex when the mood strikes
- Doesn’t interfere with orgasm or ejaculation
- High patient and partner satisfaction
- Low risk of device failure. Generally inflatable implants last
10-15 years. It is possible to replace them in case the device
fails.
Ejaculatory dysfunction: Premature ejaculation, Retrograde
ejaculation, Anejaculation
Premature Ejaculation:
Premature ejaculation is when semen
is released sooner than a man or his partner would like. PE might
not be a cause for worry. But, PE can be frustrating if it makes sex
less enjoyable and impacts your relationship.
A study looking at 500 couples from five different countries found
the average time taken to ejaculate during intercourse was around 5
minutes. However, it's up to each couple to decide if they’re happy
with the time taken – there’s no definition of how long sex should
last. Occasional episodes of premature ejaculation are common and
aren't a cause for concern. However, if you're finding that around
half of your attempts at sex result in premature ejaculation, it
might help to get treatment.
There are many reasons why men have PE. There can be biological,
chemical and/or emotional reasons. There may be issues with the
brain signals that rule sexual excitement.
Common treatments are behavioral therapy, tablets and creams. Many
people try more than one option at the same time.
- Behavioural Therapy: Makes men aware of the feelings that lead
to the climax, so they can delay ejaculation. The goal is to
train your body and increase control. The stop-start method is
when you stop stimulation, regain control and then start again.
You will need your partner’s help with these exercises.
- Medical Therapy: They lower serotonin levels. You’ll usually be
advised to take it one hour before sex, but not more than once a
day. Your response to the treatment will then be reviewed after
four weeks (or after six doses) and again every six months.
- Numbing Creams or Sprays: There are creams and sprays that you
can put on the head and shaft of the penis before sex to lower
sensation. They also cause vaginal numbness, so they should be
washed off before sex.
Retrograde Ejaculation:
It happens when semen travels
backward into the bladder instead of through the urethra (the tube
that urine passes through).
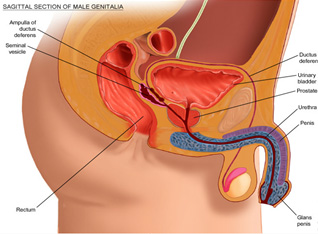
Men with retrograde ejaculation still experience the feeling of an
orgasm and the condition doesn't pose a danger to health. However,
it can affect the ability to father a child.
Prostate gland surgery or bladder surgery is the most common cause of
retrograde ejaculation. Other causes are diabetes, multiple
sclerosis and a class of medicines known as alpha-blockers, which
are often used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
Most men do not need treatment for retrograde ejaculation because
they are still able to enjoy healthy sex life and the condition does
not have adverse effects on their health.
Men who want to have children can have sperm taken from their urine
for use in artificial intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in-vitro
fertilization (IVF).
Anejaculation
Anejaculation is the inability to ejaculate
semen despite stimulation of the penis by intercourse or
masturbation. If anejaculation is caused by medications, stopping
the medicine will most likely restore normal function.
Vibrostimulation: The vibrator acts by providing a strong stimulus
for a long duration (20-30min) to the penis. Vibrator stimulation
results in ejaculation in about 60% of men suffering from a
neurological (spinal cord) injury. This is a simple and quite
effective way of retrieving semen in order to proceed with
artificial insemination (inserting sperm directly into the uterus).
Low testosterone (Hypogonadism)
Male hypogonadism means the testicles do not produce enough of the
male sex hormone testosterone. When levels are low, men might have
decreased sex drive, less muscle mass, erectile dysfunction and
fatigue. Testosterone is responsible for male reproductive and
sexual functions. It affects puberty, fertility, muscle mass, body
composition, bone strength, fat metabolism, sex drive, mood and
mental processes.

Types of Hypogonadism:
Primary hypogonadism is caused by a
problem in the testes. This type is most frequent and usually
affects development in childhood and adolescence.
Secondary
hypogonadism is caused by a problem in glands (pituitary gland,
hypothalamus) that tell the testes to make testosterone. This type
is more common among older men.

Symptoms:
Hypogonadism can occur at any age. The symptoms
will be different depending on your age when it develops. Common
symptoms in adult men include:
- Fatigue
- Hot flushes
- Low sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction
- Mood changes
- Difficulty concentrating
- Problem in sleeping
- Loss of muscle mass
- Decreased bone density
- Enlarged breasts
- Loss of body hair
- Infertilit
Diagnosis:
Male hypogonadism is diagnosed based on:
- Long-term discomfort from symptoms
- Low testosterone levels in the blood
- Size of the testes on clinical examination
Treatment:


Penile curvature / Peyronie’s disease:
Penile curvature could be from birth (congenital penile curvature) or
acquired later in life (Peyronie’s Disease). One will usually notice
a curved penis only during the penile erection and not when the
penis is flaccid (resting state).
Congenital penile curvature although present since birth will become
obvious during erection when he reaches puberty or early adult life.
Peyronie’s Disease is caused by the way a person’s body heals wounds.
Injury or damage to the outer tissues of the penis causes scar-like
tissue (plaque) to form.

“Peyronie’s was named after the French surgeon François
Gigot de La Peyronie, who described it in
1743”

PEYRONIE’S DISEASE IS NOT A DISEASE YOU CAN CATCH FROM
SOMEONE ELSE AND IT IS NOT CAUSED BY ANY KNOWN DISEASE THAT
CAN BE PASSED TO OTHERS.

Peyronie’s disease usually occurs in two phases — the acute
(or active) phase and the chronic (or stable) phase. The first
painful phase can last up to about 18 months. For most men, the
chronic or stable phase begins 12-18 months after symptoms
first appear.
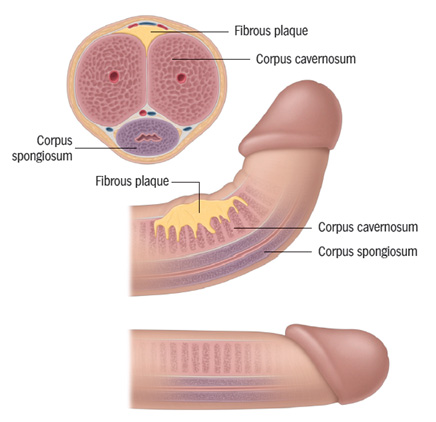
Fig: Peyronie’s disease with penile curvature and
plaque
Signs of Peyronie’s disease may involve:
- A curve in the penis
- Hard lumps on one or more sides of the penis
- Painful erections
- No or soft erections
- Spontaneous-sex when the mood strikes
- Having trouble with sex or having sex that hurts because of a
bent/curved penis

Treatment:
Andrologists may treat Peyronie’s using non-surgical or surgical
treatments.
Non-surgical treatments may include tablets, penile traction devices
and shots/injections directly into the plaque which brings higher
doses of the drug directly to the problem.
Surgery is an option for men with severe penile curvature that find
it difficult to have sex. There are three surgeries used to help men
with Peyronie’s Disease:
- Making the side of the penis opposite the plaque shorter
(Plication surgery)
- Making the side of the penis with plaque longer with a graft
(Graft surgery)
- Making the penis straight with a prosthetic device (penile
implant)

Penile enlargement surgeries
- Penile fillers
- Suprapubic fat reduction
- Pubic lipectomy
- Pubic liposuction
- Penile implant and multiple corporotomy incisions
Priapism
Priapism is a rare condition involving an erection that lasts for an
unusually long time. It can be painful. This type of erection is not
related to sexual stimulus. Immediate treatment is important to
prevent tissue damage and erectile dysfunction (ED).

Priapism got the name from Priapus. Roman statue showing Priapus –
the god of fertility. The distinguishing feature of the deity is the
great erect penis, which was to symbolize the economic well-being of
the owners of the House of the Vettii in Pompeii.
There are two types of priapism:
- Ischemic priapism: When blood cannot leave the penis. This
erection can last for more than four (4) hours. The penis shaft
may be very hard, while the tip is soft. It is known to cause
pain and discomfort. This type may stop and start (stuttering
priapism).
- Nonischemic priapism: When too much blood flows into the penis.
This is a less painful erection, but it can also last for more
than four (4) hours. The penis shaft is erect but not rigid.
Priapism can happen in young boys (age 5-10), young adults (around
age 20) and mature men (over age 50).
Priapism happens when blood flow to the penis doesn’t work correctly.
Some things that could cause this are:
- Blood disorders, like sickle cell anemia and leukemia
- Prescription drugs, like some ED drugs, e.g. Sildenafil
(Viagra), Tadalafil, mental health drugs, e.g. Fluoxetine,
Bupropion, Risperidone and Olanzapine and blood thinners, e.g.
Warfarin and Heparin
- Alcohol and drug use
- Injury to your genitals, pelvis or the area between the penis
and the anus or to the spinal cord
- Tumours
WHY IS TREATMENT IMPORTANT?
When an erection lasts for too
long, the blood becomes trapped in the penis. The blood trapped in
the penis is unable to go to other parts of the body. The lack of
oxygen can damage or destroy tissue in the penis. This can disfigure
the penis. It may also cause problems like erectile dysfunction
(when the penis cannot become erect) in the future.
Treatment:
Ischemic priapism (most common, 95%) calls for emergency care. Blood
must be drained from the penis. There are several ways to do this:
- Aspiration (when a surgical needle and syringe is used) to drain
excess blood
- Medicine or a saline mix may be injected into penile veins to
improve blood flow. The veins are flushed to relieve pain,
remove oxygen-poor blood and stop the erection
- A surgeon may perform a “shunt” to vent blood from the penis or
penile implant surgery if presented beyond 36 hours of having
priapism.
Nonischemic priapism (less common, 5%) often goes away without
treatment. Simple ice and pressure on the perineum may help end the
erection. A watch and wait approach is used before surgery.